|
Bio-Community
Human Development /
Smart Growth / Biotechnology & Community
/Food Analysis Testing
Services Items/CRO/CMO Services, Assets Services ..
Human development(humanity)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_development_(humanity)
Development concerns expanding the choices people have,
to lead lives that they value, and improving the human condition so that people
have the chance to lead full lives.[2] Thus, human
development is about much more than economic growth, which is only a means of
enlarging people’s choices.[3] Fundamental
to enlarging these choices is building human capabilities —the
range of things that people can do or be in life. Capabilities are "the
substantive freedoms [a person] enjoys to lead the kind of life [they have]
reason to value".[4] Human
development disperses the concentration of the distribution of goods and
services that underprivileged people need and center its ideas on human
decisions.[5] By investing
in people, we enable growth and empower people to pursue many different life
paths, thus developing human capabilities.[6] The most
basic capabilities for human development are: to lead long and healthy lives, to
be knowledgeable (i.e., educated), to have access to resources and social
services needed for a decent standard of living, and to be able to participate
in the life of the community. Without these,
many choices are simply not available, and many opportunities in life remain
inaccessible.[3]

|
An abstract illustration of human capability is a bicycle. A bicycle itself is a
resource- a mode of transportation. If the person who owns the bicycle is unable
to ride it (due to a lack of balance or knowledge), the bicycle is useless to
that person as transportation and loses its functioning. If, however, a person
both owns a bicycle and has the ability to ride a bicycle, they now have the
capability of riding to a friend's house, a local store, or a great number of
other places. This capability would (presumably) increase their value of life
and expand their choices. A person, therefore, needs both resources and the
ability to use them to pursue their capabilities. This is one example of how
different resources or skills can contribute to human capability. This way of
looking at development, often forgotten in the immediate concern with
accumulating commodities and financial wealth, is not new. |
|
Virtuous circle and vicious circle
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtuous_circle_and_vicious_circle

The terms virtuous
circle and vicious circle (also
referred to as virtuous cycle and vicious
cycle) refer to complex chains of events which
reinforce themselves through a feedback
loop.[1] A virtuous circle has favorable
results, while a vicious circle has detrimental
results.
Both circles are complexes of events with no tendency towards equilibrium (social, economic, ecological,
etc.) - at least in the short run. Both systems of events have feedback loops in
which each iteration of the cycle reinforces the previous one (positive feedback).
These cycles will continue in the direction of their momentum until an external
factor intervenes and breaks the cycle.
A well-known example of a vicious circle in economics is hyperinflation.
Examples:
Vicious circles in the subprime mortgage crisis
The contemporary subprime mortgage
crisis is
a complex of vicious circles, both in its genesis and in its manifold outcomes,
most notably the late 2000s recession.
A specific example is the circle related to housing. As housing prices decline,
more homeowners go "underwater",
when the market value of a home drops below the mortgage on it. This provides an
incentive to walk away from the home, increasing defaults and foreclosures.
This, in turn, lowers housing values further from over-supply, reinforcing the
cycle.[2]
The foreclosures reduce the cash flowing into banks and the value of
mortgage-backed securities (MBS) widely held by banks. Banks incur losses and
require additional funds, also called “recapitalization”. If banks are not
capitalized sufficiently to lend, economic activity slows and unemployment increases,
which further increase the number of foreclosures.
Economist Nouriel Roubini described
the vicious circles within and across the housing market and financial markets
during interviews with Charlie Rose in
September and October 2008.[3][4][5]
|
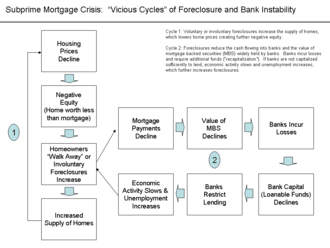
Vicious cycles in the subprime mortgage crisis |
Other
Other examples include the poverty cycle, sharecropping,
and the intensification of drought.
|
Smart growth
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smart_growth

|
Smart growth is an urban planning and transportation theory
that concentrates growth in compact walkable urban centers to avoid sprawl. It also advocates
compact, transit-oriented, walkable, bicycle-friendly land
use, including neighborhood schools, complete streets, and mixed-use
development with a range of housing choices.[1] The term
'smart growth' is particularly used in North America. In Europe and particularly
the UK, the terms 'Compact City' or 'urban
intensification' have often been used to describe similar concepts, which have
influenced government planning policies in the UK, the Netherlands and several
other European countries. |
Smart growth values long-range, regional considerations of sustainability over
a short-term focus. Its sustainable
development goals are to achieve a unique sense of community
and place; expand the range of transportation, employment, and housing choices;
equitably distribute the costs and benefits of development; preserve and enhance
natural and cultural resources; and promote public health.
Basic concept
Smart growth is related to, or may be used in combination with the following
concepts:

The smart growth approach to development is multifaceted
and can encompass a variety of techniques. For example, in the state of Massachusetts smart
growth is enacted by a combination of techniques including increasing housing
density along transit nodes, conserving farm land, and mixing residential and
commercial use areas.[4] Perhaps the
most descriptive term to characterize this concept is Traditional
Neighborhood Development, which recognizes that smart growth and related
concepts are not necessarily new, but are a response to car culture and sprawl.
Many favor the term New Urbanism, which
invokes a new, but traditional way of looking at urban planning.
There are a range of best practices associated with smart
growth, these include: supporting existing communities, redeveloping
underutilized sites, enhancing economic competitiveness, providing more
transportation choices, developing livability measures and tools, promoting
equitable and affordable housing, providing a vision for sustainable growth,
enhancing integrated planning and investment, aligning, coordinating, and
leveraging government polices, redefining housing affordability and making the
development process transparent.[5]
Related, but somewhat different, are the overarching
goals of smart growth, and they include: making the community more competitive
for new businesses, providing alternative places to shop, work, and play,
creating a better "Sense of Place," providing jobs for residents, increasing
property values, improving quality of life, expanding the tax base, preserving
open space, controlling growth, and improving safety.[6]
Biotechnology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biotechnology
|
|
Biotechnology is the use of living systems and organisms to develop or
make products, or "any technological application that uses biological systems,
living organisms, or derivatives thereof, to make or modify products or
processes for specific use" (UN Convention on Biological Diversity, Art. 2).[1]Depending on
the tools and applications, it often overlaps with the (related) fields of bioengineering, biomedical
engineering , biomanufacturing, molecular
engineering, etc.
For thousands of years, humankind has used biotechnology
in agriculture, food production, and medicine.[2] The term is
largely believed to have been coined in 1919 by Hungarian engineer Károly Ereky. In the late
20th and early 21st centuries, biotechnology has expanded to include new and
diverse sciencessuch as genomics, recombinant gene techniques,
applied immunology, and development
of pharmaceutical therapies
and diagnostic
tests.[2]
|
|

Insulin crystals |
History
|
Although not normally what first comes to mind, many forms of human-derived agriculture clearly
fit the broad definition of "'utilizing a biotechnological system to make
products". Indeed, the cultivation of plants may be viewed as the earliest
biotechnological enterprise.
Agriculture has been theorized to have become the dominant way of
producing food since the Neolithic Revolution.
Through early biotechnology, the earliest farmers selected and bred the best
suited crops, having the highest yields, to produce enough food to support a
growing population. As crops and fields became increasingly large and difficult
to maintain, it was discovered that specific organisms and their by-products
could effectively fertilize, restore nitrogen,
and control pests. Throughout
the history of agriculture, farmers have inadvertently altered the genetics of
their crops through introducing them to new environments and breeding them
with other plants — one of the first forms of biotechnology.
|

Brewing was
an early application of biotechnology |
Examples
|
Biotechnology has applications in four major industrial areas, including health
care (medical), crop production and agriculture, non food (industrial) uses of
crops and other products (e.g. biodegradable
plastics, vegetable oil, biofuels), and environmental
uses.
For example, one application of biotechnology is the directed use of organisms for
the manufacture of organic products (examples include beer and milk products).
Another example is using naturally present bacteria by the
mining industry in bioleaching. Biotechnology
is also used to recycle, treat waste, clean up sites contaminated by industrial
activities (bioremediation), and
also to produce biological weapons.
|

A rose plant
that began as cells grown in a tissue culture |
|
A series of derived terms have been coined to identify
several branches of biotechnology ; for example:
-
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field which addresses biological
problems using computational techniques, and makes the rapid organization as
well as analysis of biological data possible. The field may also be referred to
as computational biology, and can be defined as,
"conceptualizing biology in terms of molecules and then applying informatics
techniques to understand and organize the information associated with these
molecules, on a large scale."[16] Bioinformatics
plays a key role in various areas, such as functional genomics, structural genomics,
and proteomics, and forms a key
component in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sector.
-
Blue biotechnology is a term that has been used to describe the marine and
aquatic applications of selection and domestication of plants via micropropagation.
Another example is the designing of transgenic plants to
grow under specific environments in the presence (or absence) of chemicals. One
hope is that green biotechnology might produce more environmentally friendly
solutions than traditional industrial
agriculture. An example of this is the engineering of a plant to express a pesticide, thereby ending
the need of external application of pesticides. An example of this would be Bt corn. Whether or
not green biotechnology products such as this are ultimately more
environmentally friendly is a topic of considerable debate.
-
Red biotechnology is applied to medical processes. Some examples are the
designing of organisms to produce antibiotics, and the
engineering of genetic cures through genetic manipulation.
-
White biotechnology, also known as industrial
biotechnology, is biotechnology applied to industrial processes.
An example is the designing of an organism to produce a useful chemical. Another
example is the using of enzymes as
industrial catalysts to
either produce valuable chemicals or destroy hazardous/polluting chemicals.
White biotechnology tends to consume less in resources than traditional
processes used to produce industrial goods.[citation
needed]
The investment and economic output of all of these types of applied
biotechnologies is termed as "bioeconomy".
|
Bioeconomy in everyday life
https://www.google.com.tw/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwjG7LGm-_3UAhXIgbwKHUQ2AZcQFggqMAA&url=https%3A%2F%2Fec.europa.eu%2Fresearch%2Fbioeconomy%2Fpdf%2Feu_bioecnomoy_apartment_katalog.pdf&usg=AFQjCNEURR7OXvaVgUZ9er3jwPnmT5R-pw

|
Whether for food, clothing or consumer goods, in the kitchen or in the garage –
many everyday products contain components made from renewable raw materials or
are produced using biobased procedures. The bioeconomy has thus made its way
into everyone's lives, even though we’re not usually aware of it.
According to experts, bioeconomy is “… the knowledge-based production and use of
renewable resources to make products, processes and services available for
various economic sectors.”
For this reason, the bioeconomy makes an important contribution by linking
economic growth with environmental sustainability. In view of depleting
fossil-based resources, climate change and a growing world population,
sustainable resource-efficient strategies are in demand to guarantee the
well-being of modern societies. Which is why the bioeconomy is of central
importance in all economic sectors.
|
Bio-Community(Global & Local)
List of largest biotechnology & pharmaceutical companies
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_largest_biotechnology_%26_pharmaceutical_companies
Graphical representation:
.png)
List of largest pharmaceutical companies by revenue
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_largest_pharmaceutical_companies_by_revenue
2016 Biotechnology Industry in Taiwan(White Paper)
http://www.biopharm.org.tw/download/Biotechnology_Industry_in_Taiwan_2016.pdf
2017 Introduction to Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical
Industries in Taiwan
http://www.govbooks.com.tw/books/110917
2017 Introduction to Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical
Industries in Taiwan, Republic of China
https://www.biopharm.org.tw/download/2017 Introduction to Biotechnology and
Pharmaceutical Industries in Taiwan, Rep. of China.pdf
2017 Taiwan White Paper - AmCham Taipei
https://amcham.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/June-2017-Taiwan-Business-TOPICS.pdf
Directory
I. Niche to invest in Taiwan's biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry
1. Development environment for Taiwan's biotechnology and pharmaceutical
industry
2. Overview for Taiwan's biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry.
II. Infrastructure for Taiwan's biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry
1. Research and Development
2. Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Investments
3. Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Talents
4. Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Incubation
5. Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Cluster
III. Institutions to assist in investing Taiwan's biotechnology and
pharmaceutical industry
1. Biotechnology & Pharmaceutical Industries Promotion Office, MOEA (BPIPO)
2. The Executive Yuan's One-Stop-Service Office for Biotechnology Industry
IV. Related measures for investment incentives and loans
1. Investment incentives
2. Low-interest loans
3. Government fund injection
4. Publicly traded recommended
|

|
V. Outlook
Appendix 1: Industry Regulations
Appendix 2: Track of promoting Taiwan's biotechnology and pharmaceutical
industry
Appendix 3: Domestic and Overseas Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Related
Service Agencies
Biotech Industry in Taiwan
https://www.google.com.tw/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwjWidqJjf7UAhWDn5QKHW3DDuAQFgg5MAE&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww3.nccu.edu.tw%2F~hmlien%2FEconomics%2520and%2520Social%2520Change%2520in%2520Taiwan%2Flecture%2F20161028BioTechIInTaiwan-Shia1011a.pdf&usg=AFQjCNG4z6MNvFjdhV2E6h1_PsIRIYg-tg



Food Analysis Services:
(ABDC) Food Analysis Testing Services Items:
FoodAnalysisTestingServicesItems.aspx
Food science:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_science
Food chemistry:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_chemistry
Food quality:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_quality
Analytical chemistry:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analytical_chemistry
Food sampling:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_sampling
Nutrition analysis:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nutrition_analysis
Particle size analysis:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Particle_size_analysis.
Ingredient
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ingredient
Food additive:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_additive
List of food additives:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_food_additives
Overview of Food Ingredients, Additives & Colors:
https://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/FoodAdditivesIngredients/ucm094211.htm
Food Additive Status List:
https://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/FoodAdditivesIngredients/ucm091048.htm
Food defense:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_defense
https://www.fda.gov/food/fooddefense/default.htm
Eating Healthy:
https://cspinet.org/eating-health
NutritionAction - Unbiased advice to help you eat healthfully and live longer:
https://www.nutritionaction.com/
CRO/CMO Services:
Definitions
Contract research organization:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contract_research_organization
Contract manufacturing organization:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contract_manufacturing_organization
Partner references:
(constructing....)
Assets Services:
Definitions
Real estate:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real_estate
Real Estate in the Real Economy:
http://www.epra.com/media/Real_estate_in_the_real_economy_-_EPRA_INREV_report_1353577808132.PDF
Science park:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Science_park
Industrial park:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_park
Industrial district:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_district
Resource and Environmental construction in Taiwan
& Taichung
Economy of Taiwan:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Taiwan
Transportation in Taiwan:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transportation_in_Taiwan
List of metropolitan areas in Taiwan:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_metropolitan_areas_in_Taiwan
List of companies of Taiwan:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_companies_of_Taiwan
Taichung:
Park:
http://www.ctsp.gov.tw/english/01about/abo_future_prospects.aspx?v=20&fr=768&no=769
Central Taiwan Science Park:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_Taiwan_Science_Park,
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/中部科學工業園區臺中工業區
Taichung Industrial Park:
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E8%87%BA%E4%B8%AD%E5%B7%A5%E6%A5%AD%E5%8D%80
Promoting cases:
(constructing....)
|