|
|
牙科掃描儀及設計軟體
CAD/CAM 牙科簡介
CAD/CAM Dentistry(From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAD/CAM_Dentistry
CAD/CAM dentistry is a field of dentistry and prosthodontics using CAD/CAM
(computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing) to improve the design
and creation of dental restorations,[1][2] especially dental prostheses,
including crowns, crown lays, veneers, inlays and onlays, fixed bridges, dental
implant restorations, dentures (removable or fixed), and orthodontic appliances.
CAD/CAM 牙科在牙科和口腔修復中使用CAD/CAM(計算機輔助設計/計算機輔助製造)以增進牙齒修復的設計和創作的一個領域[1] [2], 尤其是假牙,
包括牙冠, 冠嵌體, 貼片, 嵌體和高嵌體, 固定牙橋, 種植牙修復體, 義齒(可移動或固定), 以及正畸矯治器等.

CAD/CAM complements earlier technologies used for these purposes by any
combination of increasing the speed of design and creation; increasing the
convenience or simplicity of the design, creation, and insertion processes; and
making possible restorations and appliances that otherwise would have been
infeasible.
CAD/CAM 以增加設計和創造速度的任何組合, 增加了設計, 創建和置入過程的方便或簡單程度, 補充了用於這些目的的早期技術,
並且使得早期不可行的修復技術和器具成為可能.
Other goals include reducing unit cost and making affordable restorations and
appliances that otherwise would have been prohibitively expensive.
However, to date, chairside CAD/CAM often involves extra time on the part of the
dentist, and the fee is often at least two times higher than for conventional
restorative treatments using lab services.
Like other CAD/CAM fields, CAD/CAM
dentistry uses subtractive processes (such as CNC milling) and additive
processes (such as 3D printing) to produce physical instances from 3D models.
其他目標包括降低單位成本, 使能得到如果不這樣做就只會是昂貴的修復和器具.
然而, 迄今為止, 診療椅旁CAD/CAM經常涉及對牙醫師的一部分額外的時間, 而其費用經常是比使用實驗室服務的常規修復治療高至少2倍.
像其他的CAD/ CAM領域, 牙科CAD/CAM 採用減法(如數控銑床)和加法的過程(如3D列印)從3D模型產製出實體.....(後續)
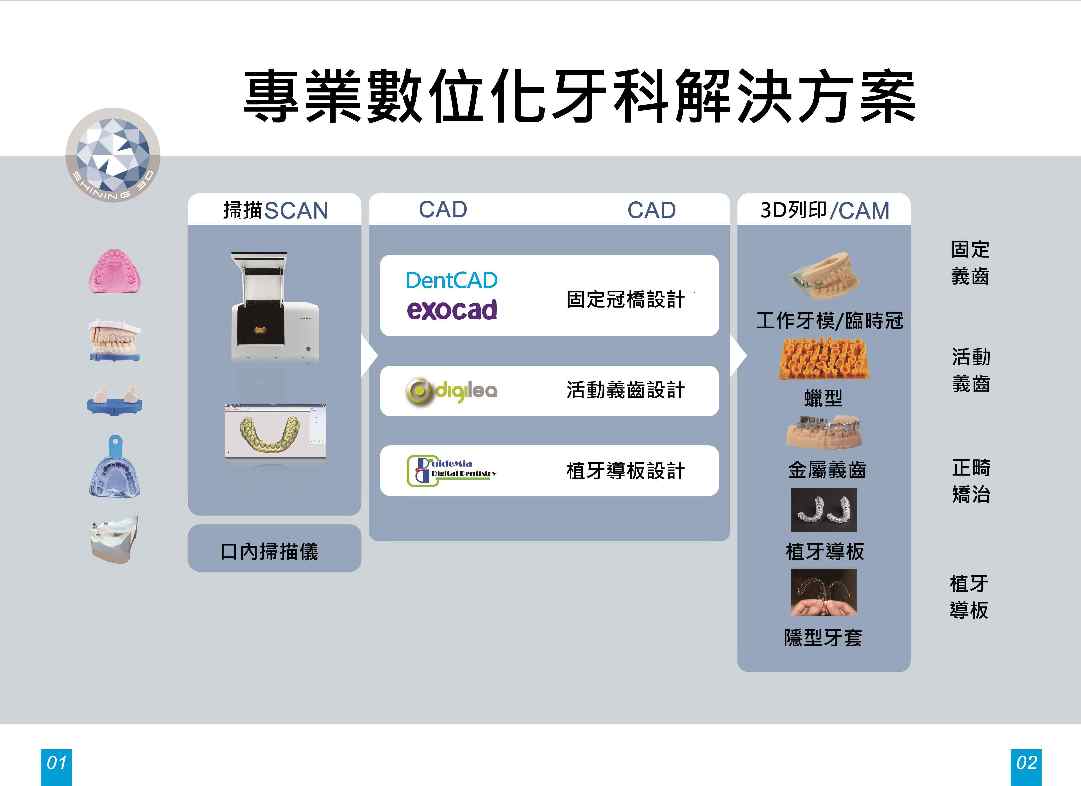
專業數位化牙科解決方案
我們(先臨三維 + ABDC)與牙科技工所, 口腔門診深入合作,
與國際知名齒科設計軟體公司,
台灣本地的精密牙科機械加工廠, 3D列印機廠商聯合, 不斷提升數字化技術在齒科行業的應用.
結合企業實際情況, 為各企業提供有效的數位化齒科解決方案, 幫助企業確保義齒制作的品質,
縮短製作週期, 提升義齒生產能能量.
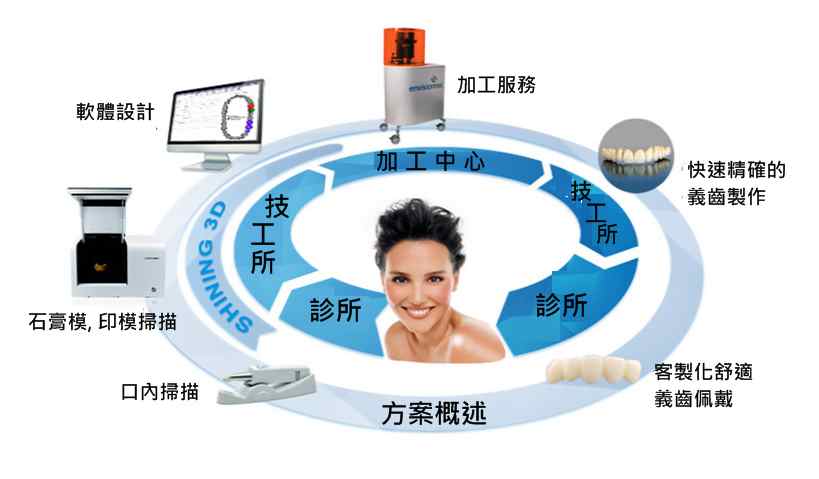
我們提供的方案能夠幫助獲取到精確的印模, 模型, 牙齒等相關3D數據, 使得醫生與技工所能夠具有更高效率的溝通,
使設計人員可以更快速地進行設計工作.
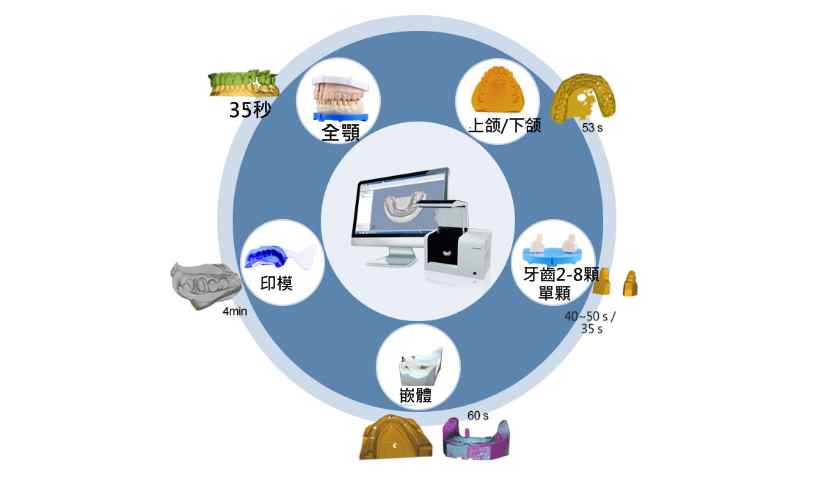
固定義齒, 活動義齒, 植牙導板的設計與制作我們提供多項一流的齒科設計系統, 可建立良好的咬合關係,
簡單快速的完成優質的修復體設計, 提供人工植牙手術規劃和手術導板的設計, 讓齒科種植手術更簡單可靠.
經由專業的齒科軟體與AutoScan義齒3D掃描儀, 可與台灣本地的精密牙科機械加工廠,
以及齒科3D列印機前後連貫, 高度整合, 進而有效的製作專業舒適的修復體.

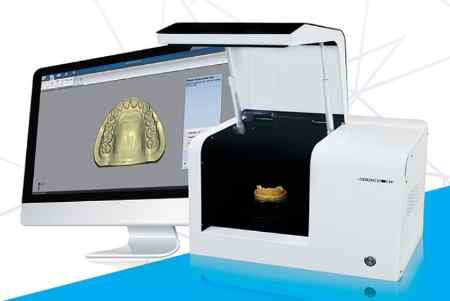
AutoScan 系列牙科掃描儀
http://www.shining3dscanner.com/en-us/product_dentalscan.html

AutoScan系列
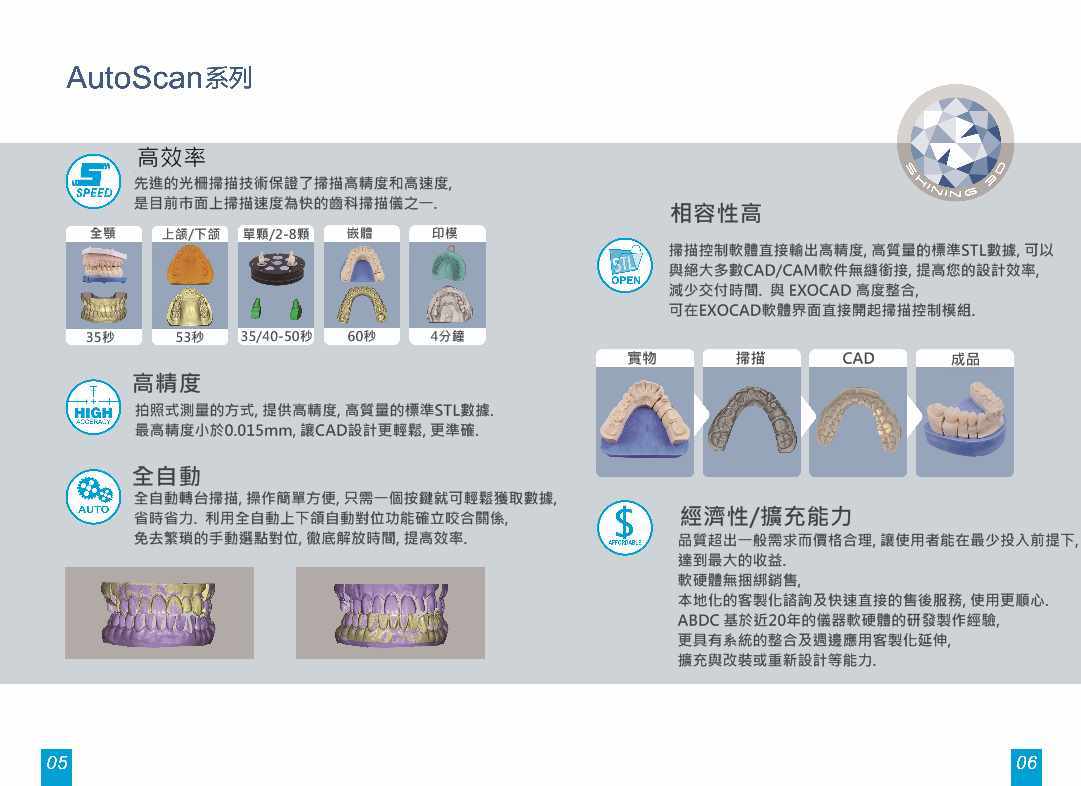
專業齒科CAD系統
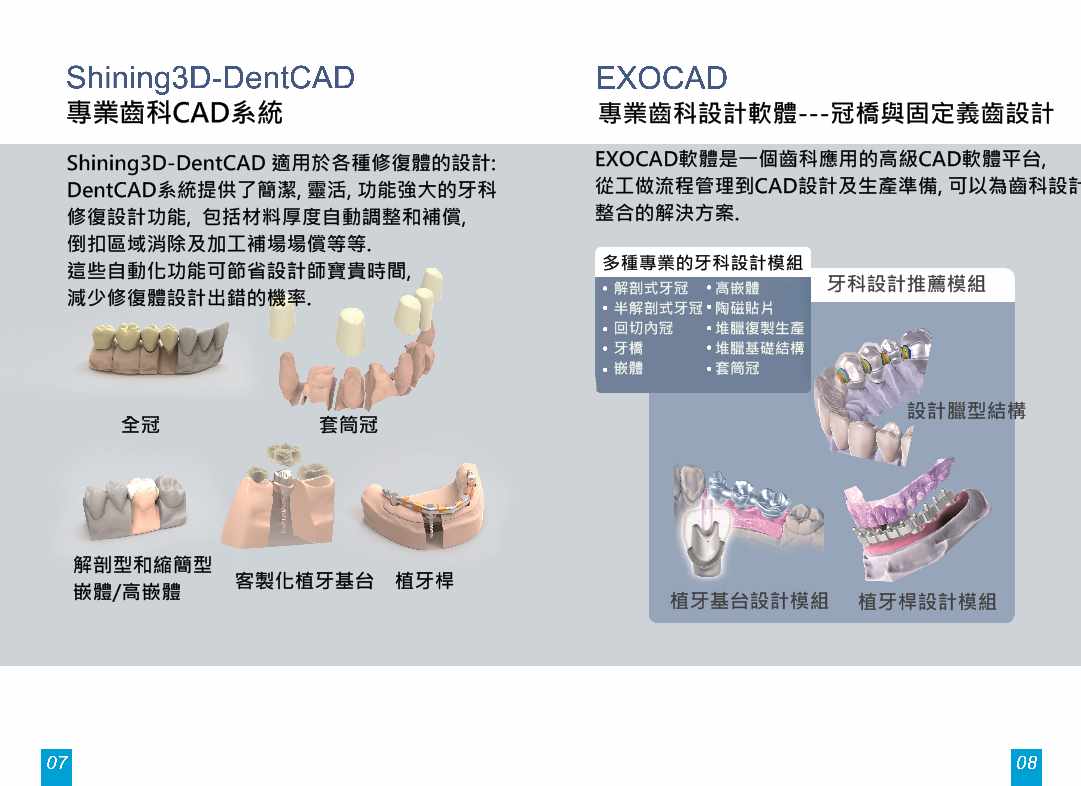
專業齒科設計軟體

CAD/CAM 牙科簡介(續)
CAD/CAM Dentistry(中英對照)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAD/CAM_Dentistry
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
CAD/ CAM牙科
Contents
1. History
2. Difference from conventional restoration
3. Process
4. Drawbacks
5. List of CAD/CAM dental software products
6. References
內容
1. 歷史
2. 與傳統修復的差異
3. 流程
4. 缺點
5. CAD/CAM牙科軟體產品列表
6. 參考文獻
History
Although CAD/CAM dentistry was used in the mid-1980s, early efforts were
considered a cumbersome novelty, requiring an inordinate amount of time to
produce a viable product.
This inefficiency prevented its use within dental offices and limited it to
labside use (that is, use within dental laboratories).
As adjunctive techniques, software, and materials improved, the chairside use of
CAD/CAM(use within dental offices/surgeries) increased.[3] For example, the
commercialization of Cerec by Siemens made CAD/CAM available to dentists who
formerly would not have had avenues for using it.
歷史
雖然牙科CAD/CAM在80年代中期以被使用的, 但早期的努力被認為新穎但卻是繁瑣的, 需要過量的時間以產生一個可行的產品.
這種低效率阻礙了它在牙科診所內的使用, 並限制其只能在實驗室內使用(即在牙科實驗室內使用).
而當相關的技術, 軟體和材料被改進後, 在診療椅旁使用CAD/CAM(牙科診所/手術中使用)增加了[3] 例如, 由西門子公司商業化製造的Cerec,
使得牙醫師可取得以前不會有途徑使用它的CAD/ CAM.
Difference from conventional restoration
Chairside CAD/CAM restoration differs from conventional dentistry in that the
prosthesis is typically luted or bonded the same day.
Conventional prosthesis, such as crowns, have temporaries placed from one to
several weeks while a dental laboratory or in house dental lab produces the
restoration.[4] The patient returns later to have the temporaries removed and
the laboratory-made crown cemented or bonded in place.
An in-house CAD/CAM system enables the dentist to create a finished inlay in as
little as an hour in some cases.[5]
與傳統修復的差異診療椅旁CAD/CAM 的修復不同於傳統的牙科的地方, 在於假體通常是在同一天被接上或粘結.
傳統假體, 如牙冠, 當一個牙科實驗室或在室內的牙科實驗室在製作修復體時, 需置入臨時假體一到幾個星期[4]. 病患之後回來做臨時假體的移除,
以將實驗室製做的牙冠鞏固或粘結到位置上.
一個室內的CAD/CAM系統, 在一些情況下, 可以讓牙醫師在短短的一個小時做好一個完整的嵌體[5].
Bonded veneer CAD/CAM restorations are more conservative in their preparation of
the tooth.
As bonding is more effective on tooth enamel than the underlying dentin, care is
taken not to remove the enamel layer.
Designed to provide a complete digital workflow, chairside dental CAD/CAM
systems include a digital impression system, 3D dental design software and a
chairside mill that function as a single system.
Designed to provide a seamless workflow, these systems allow you to provide
patients with crowns, inlays, onlays and veneers in a single appointment.
Though one-day service is a benefit that is typically claimed by dentists
offering chairside CAD/CAM services, the dentist's time is commonly doubled and
the fee is therefore doubled.
黏結陶瓷貼片的CAD/CAM修復在其牙齒的製備上是比較更保守的.
由於在牙齒的牙釉質上做粘結比在牙本質更有效, 要小心不要移除了牙釉質.
為提供一個完整的數位化工作流程而設計, 診療椅旁CAD/CAM 的修復系統包括數位印模系統, 牙科3D設計軟體和診療椅旁研磨機成為一個單一功能的系統.
為提供一個密切的工作流程而設計,這些系統允許您能在一次的約診內, 提供給患者牙冠, 嵌體, 高嵌體和貼面.
雖然, 一天的服務 是提供診療椅旁CAD/CAM 的牙醫師典型訴求的好處, 牙醫師所用的時間通常是加倍, 因此費用也增加倍了.
Process
Typically CAD/CAM dental restorations are milled from solid blocks of ceramic or
composite resin that closely match the basic shade of the restored tooth.
Metal alloys may also be milled or digitally produced.
After decayed or broken areas of the tooth are corrected by the dentist, an
image (scan) is taken of the prepared tooth and the surrounding teeth. This
image, called a digital impression, draws the data into a computer. Proprietary
software then creates a replacement part for the missing areas of the tooth,
creating a virtual restoration.
This is called reverse engineering.
程序
通常CAD/CAM的牙科修復體是由與要修復的牙的齒基本型狀很接近的陶瓷或複合樹脂固體塊狀研磨而成.
金屬的合金也可以被研磨或以數位方式產生.
在牙齒蛀損或破碎後的區域由牙醫師修正之後, 取得了製備的牙齒和周圍牙齒的圖像(掃描). 這一圖像, 稱為數位印模, 將數據建置到計算機內.
然後專用軟體在牙齒缺失的區域創造了一個更換部件, 創造珠一個虛擬的修復體.
這是所謂的逆向工程.
The software sends this virtual data to a milling machine where the replacement
part is carved out of a solid block of ceramic or composite resin.
Stains and glazes are fired to the surfaces of the milled ceramic crown or
bridge to correct the otherwise monochromatic appearance of the restoration.
The restoration is then adjusted in the patient's mouth and cemented or bonded
in place. As in other fields, additive manufacturing (3D printing) first entered
CAD/CAM dentistry in the form of laboratory experiments, but its use has since
expanded; and chairside use, although not yet widespread, is advancing.
這個軟體將這這個虛擬的數據送到銑床, 其中(牙齒)要更換的部分是從陶瓷或複合樹脂的固體塊雕刻出來.
接著色料和釉料被施加在瓷牙冠或牙橋的表面, 以改變的修復體原來單調的外觀.
然後修復體在患者的口腔內加以調整, 以及膠合或粘合到位.
正如在其他領域, 加法的製造(3D列印), 首先是以實驗室實驗的形式進入CAD/CAM牙科, 但它的使用已經擴展開來, 而其在診療椅旁的使用, 雖然還沒有普及,
也正在推進中.
Drawbacks
As machine-built substitutes, CAD/CAM treatments have some aesthetic drawbacks,
whether they are created at the dental practice or outsourced to a dental
laboratory fabricating service.
Because the superficial layers are typically 60 to 100 micrometers (µm) in
thickness, they are not comparable to traditionally fabricated dental
restorations, which have multiple layers that are between 25 to 50 micrometers
thick.
Likewise, they rely on superficial staining to achieve a more natural
appearance, unlike hand-layered porcelain restorations, which possess a deep-set
coloration due to the multi-layering. ]
缺點
如同於機器製造的替代品, 無論是在牙科診所內製造或外包給一個牙科實驗室製造服務, CAD/CAM的處理有一定的美學缺點,
由於其表層通常是60至100微米(μm)的厚度, 它們沒能與傳統製造的牙齒修復體比較, 它們有25到50微米厚之間的多層體.
同樣他們依靠表層的染色以達到更自然的外觀, 不像手工層疊的瓷修復體, 由於多層, 它具具有一個深層的著色感.
However, traditional restorations also vary in aesthetic value.
In some hand-layered crowns and bridges, feldspathic porcelain is fused to
glass-infiltrated aluminum oxide (alumina) or zirconium-oxide (zirconia)
creating a high-strength, highly aesthetic, metal-free crown or bridge. In other
traditional restorations, this porcelain is layered onto a metal substructure
and often display color brightness, an opaque "headlight", and dark oxide lines
(a "black line" in the vicinity of the gum line).
As these dark metal substructures are not conducive to a natural appearance,
metal-free restorations are typically more aesthetically pleasing to the
patient.[6]
然而, 傳統的修復也有各不相同的美觀價值.
在一些手工層疊牙冠和牙橋, 長石瓷被熔合到玻璃滲透氧化鋁(alumina)或氧化鋯(zirconia), 產出高強度, 高美觀, 不含金屬的牙冠或牙橋.
在其他傳統的修復體, 這種陶瓷層疊在一個金屬子結構, 而且通常顯示彩色的明亮度, 不透明的"頭燈亮光", 和暗氧化物線("黑線", 在牙齦線的附近).
由於這些暗色的金屬子結構是不利於自然的外觀, 不含金屬的修復體通對患者是常較為美觀愉悅的.
There are also different medical repercussions for each restorative technique.
If the CAD/CAM restorative material is zirconia or lithium disilicate, the
restoration becomes "radio-opaque", just as metal restorations are, blocking
x-rays.
Only alumina and some composite resin materials are "radio-lucent", allowing
dentists to track potential decay.
Zirconia, lithium disilicate, conventional porcelain-to-metal, and traditional
gold and other all-metal crowns block x-ray radiation, disallowing evaluation
over time.
Finally, the accuracy of restorations using CAD/CAM technology is not as
consistent as in other dental fabricating processes.
Crowns and bridges require an extremely precise fit on tooth abutments or
stumps. Scanning and mathematically calculating the stump surface topography has
accuracy limitations, as does milling by computer-numeric-control (CNC)
machines.
不同的修復技術有不同的醫療後果.
如果在CAD / CAM用修復材料是氧化鋯或二矽酸鋰時,修復成為“不透輻射的", 就像金屬修復體一樣, 阻擋X射線.
只有氧化鋁和一些複合樹脂材料是“透輻射的", 讓牙醫跟踪電位衰減。
僅氧化鋁和一些複合樹脂材料是“無線電 - 朗訊", 讓牙醫師可以潛在的衰退.
氧化鋯, 二矽酸鋰, 傳統的瓷-金屬, 和傳統的金和其他全金屬牙冠都會阻斷X射線, 不允許隨著時間演進的評估.
最後, 使用CAD/CAM技術的修復體的精度是不如其他牙齒製備程序一致.
牙冠和牙橋需要非常精確的密合於牙橋或牙殘根. 掃描和數學計算的牙殘根表面形貌有其精度限制, 就跟以計算機數位控制(CNC)機器的車銑一樣.
Fit accuracy varies according to the CAD/CAD system utilized and from user to
user.
Some systems are designed to attain higher standards of accuracy than others and
some users are more skilled than others.
Current standards require an accuracy of fit less than 10 µm, meaning the
deviation from "perfect fit" is less than 10/1000ths of a millimeter.
Currently, CAD/CAM and Hand-Made dental processes can not consistently achieve
this kind of accuracy. Only "electrophoretic deposition" of glass-infiltrated
aluminum oxide processes can consistently produce the coveted 10 µm fit.
擬合的精確度根據所用的CAD/CAD系統, 以及不同的用戶而不同.
有些系統設計用來實現比其他系統更高的精度標準, 而一些使用者比其他人熟練度佳.
當前標準要求的擬合的精度小於10微米, 意即與"完美擬合" 的偏差小於一毫米的 10/1000.
目前, CAD/CAM和手工製作的牙科程序都不能一致程度地達到這種精度. 只有 玻璃滲透氧化鋁程序的"電泳沉積" 可以一致程度地產出令人垂涎的10微米的擬合.
List of CAD/CAM dental software products
各種CAD/CAM牙科軟體產品列表
CEREC: Software for manufacturing crowns, veneers, onlays and inlays using
different types of ceramic material.
Delcam dental solutions: For the design and manufacture of copings and bridge
frameworks, including full crowns, abutments, dental bars, inlays and onlays,
and implant bridges.
Renishaw plc CAD/CAM systems: From a company that started in industrial
metrology with patented probes.
WorkNC Dental from Sescoi: CAD/CAM for automatic machining of prosthetic
appliances, implants, bridges or dental structures.[7]
Dentca: the pioneer of CAD/CAM Denture Technology, produces high-quality
dentures through computer-
aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), proprietary 3D modeling,
and scalable 3D printing technology.
3Shape Dental System: 3D scanners and software solution for designing – models,
crowns, copings and bridge frameworks, Inlays, onlays, veneers, temporaries,
wax-ups, post and core, telescopic crowns, customized abutments, implant bars
and bridges, dentures, removable partials, splints.
Origin Intelligence: 3D Dental Scanner.
References[edit]
^ Davidowitz G, Kotick PG. (2011), "The use of CAD/CAM in dentistry.", Dent Clin
North Am 55 (3): 559–570, doi:10.1016/j.cden.2011.02.011. ^ Rekow D (1987),
"Computer-aided design and manufacturing in dentistry: a review of the state of
the art", J Prosthet Dent 58 (4): 512–516, doi:10.1016/0022-3913(87)90285-X.
^ Miyazaki, T., Hotta, Y., Kunii, J., Kuriyama, S., Tamaki, Y. (January 2009).
"A review of dental CAD/CAM: current status and future perspectives from 20
years of experience". Dent Mater Journal 28 (1): 44–56. PMID 19280967.
^ Masek, R. (January 2005). "Margin isolation for optical impressions and
adhesion". International Journal of Computer Dentistry 8 (1): 69–76. PMID
15892526. ^ Sidekick Magazine, “CAD/CAM Technology: You Can’t Afford NOT to Have
It”
^ Masek, R. (July 1999). "Reproducing natural color effects on milled ceramic
restorations". International Journal of Computer Dentistry 2 (3): 209–17. PMID
11351485. ^ Micro Manufacturing Magazine, “Dental 3- to 5-axis CAM Software”
Related Topics:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dental_prosthesis
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dental_laboratory
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lost-wax_casting
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_13485
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dental_implant
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oral_cavity
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maxilla
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_mandible
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denture
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dental_technician
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DICOM
3D牙科掃描儀及設計軟體_產品介紹.doc
|